- There are now newer security-fix releases of Python 3.6 that supersede 3.6.8 and Python 3.8 is now the latest feature release of Python 3.Get the latest releases of 3.6.x and 3.8.x here.Python 3.6.8 is planned to be the last bugfix release for 3.6.x. Following the release of 3.6.8, we plan to provide security fixes for Python 3.6 as needed through 2021, five years following its initial.
- For some reason, you may need to remove Python interpreter. But some users face issues when trying to get rid of Python package, which is why we recommend that you read a complete and safe deletion guide on how to uninstall Python on your Mac to prevent any issue.

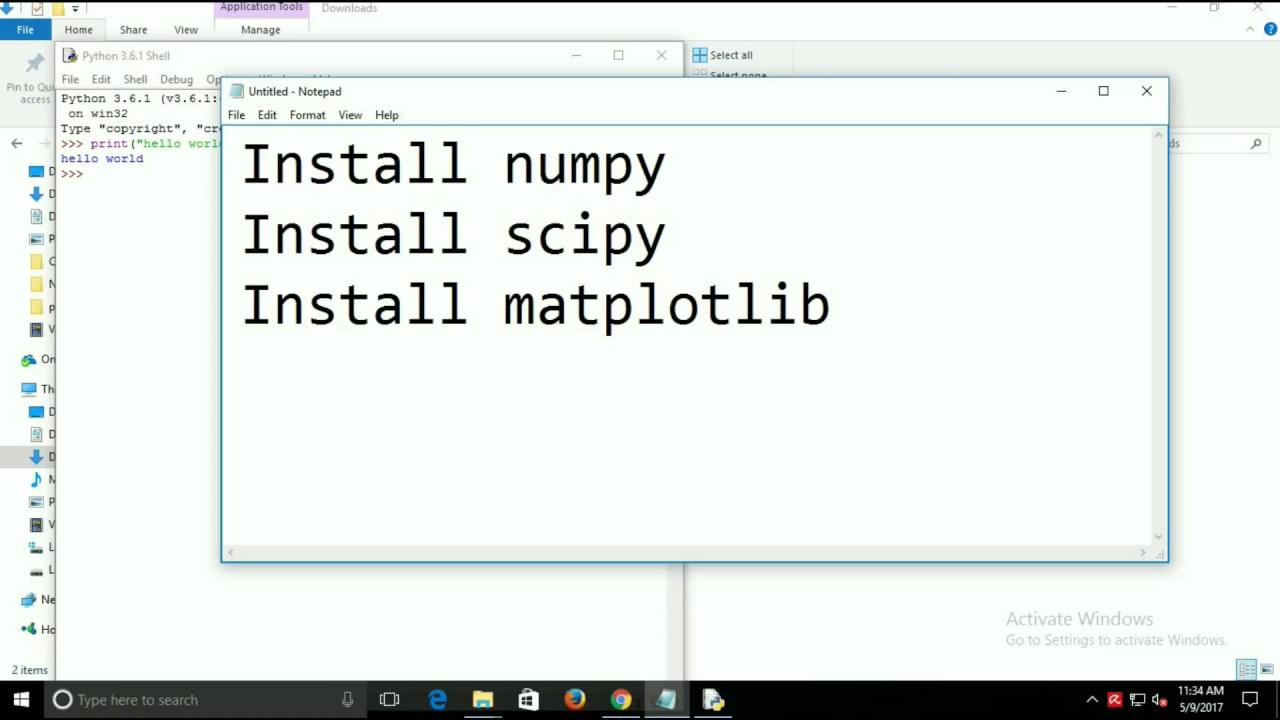
C: # Check Python λ python -V Python 3.6.4 # Check pip C: λ pip -V pip 9.0.1 from c: python36 lib site-packages (python 3.6) # Install numpy C: λ pip install numpy Collecting numpy Downloading numpy-1.14.0-cp36-none-win32.whl (9.8MB) 100% 9.8MB 83kB/s Installing collected packages: numpy Successfully installed numpy-1.14.0 # Test that. Install Numpy on Python 2.x version If you are using Python 2.x, let’s say Python 2.7, then you will have to install the Numpy using the following command. In the terminal, use the pip command to install numpy package.
Bob Savage <bobsavage@mac.com>
Python on a Macintosh running Mac OS X is in principle very similar to Python onany other Unix platform, but there are a number of additional features such asthe IDE and the Package Manager that are worth pointing out.
4.1. Getting and Installing MacPython¶
Mac OS X 10.8 comes with Python 2.7 pre-installed by Apple. If you wish, youare invited to install the most recent version of Python 3 from the Pythonwebsite (https://www.python.org). A current “universal binary” build of Python,which runs natively on the Mac’s new Intel and legacy PPC CPU’s, is availablethere.
What you get after installing is a number of things:
A
Python3.9folder in yourApplicationsfolder. In hereyou find IDLE, the development environment that is a standard part of officialPython distributions; and PythonLauncher, which handles double-clicking Pythonscripts from the Finder.A framework
/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework, which includes thePython executable and libraries. The installer adds this location to your shellpath. To uninstall MacPython, you can simply remove these three things. Asymlink to the Python executable is placed in /usr/local/bin/.
The Apple-provided build of Python is installed in/System/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework and /usr/bin/python,respectively. You should never modify or delete these, as they areApple-controlled and are used by Apple- or third-party software. Remember thatif you choose to install a newer Python version from python.org, you will havetwo different but functional Python installations on your computer, so it willbe important that your paths and usages are consistent with what you want to do.
IDLE includes a help menu that allows you to access Python documentation. If youare completely new to Python you should start reading the tutorial introductionin that document.
If you are familiar with Python on other Unix platforms you should read thesection on running Python scripts from the Unix shell.
4.1.1. How to run a Python script¶
Your best way to get started with Python on Mac OS X is through the IDLEintegrated development environment, see section The IDE and use the Help menuwhen the IDE is running.
If you want to run Python scripts from the Terminal window command line or fromthe Finder you first need an editor to create your script. Mac OS X comes with anumber of standard Unix command line editors, vim andemacs among them. If you want a more Mac-like editor,BBEdit or TextWrangler from Bare Bones Software (seehttp://www.barebones.com/products/bbedit/index.html) are good choices, as isTextMate (see https://macromates.com/). Other editors includeGvim (http://macvim-dev.github.io/macvim/) and Aquamacs(http://aquamacs.org/).
To run your script from the Terminal window you must make sure that/usr/local/bin is in your shell search path.

To run your script from the Finder you have two options:
Drag it to PythonLauncher
Select PythonLauncher as the default application to open yourscript (or any .py script) through the finder Info window and double-click it.PythonLauncher has various preferences to control how your script islaunched. Option-dragging allows you to change these for one invocation, or useits Preferences menu to change things globally.
4.1.2. Running scripts with a GUI¶
With older versions of Python, there is one Mac OS X quirk that you need to beaware of: programs that talk to the Aqua window manager (in other words,anything that has a GUI) need to be run in a special way. Use pythonwinstead of python to start such scripts.
With Python 3.9, you can use either python or pythonw.
4.1.3. Configuration¶
Python on OS X honors all standard Unix environment variables such asPYTHONPATH, but setting these variables for programs started from theFinder is non-standard as the Finder does not read your .profile or.cshrc at startup. You need to create a file~/.MacOSX/environment.plist. See Apple’s Technical Document QA1067 fordetails.
For more information on installation Python packages in MacPython, see sectionInstalling Additional Python Packages.
4.2. The IDE¶
MacPython ships with the standard IDLE development environment. A goodintroduction to using IDLE can be found athttp://www.hashcollision.org/hkn/python/idle_intro/index.html.
4.3. Installing Additional Python Packages¶
There are several methods to install additional Python packages:
Packages can be installed via the standard Python distutils mode (
pythonsetup.pyinstall).Many packages can also be installed via the setuptools extensionor pip wrapper, see https://pip.pypa.io/.
4.4. GUI Programming on the Mac¶
There are several options for building GUI applications on the Mac with Python.
Python Numpy Download Windows 10
PyObjC is a Python binding to Apple’s Objective-C/Cocoa framework, which isthe foundation of most modern Mac development. Information on PyObjC isavailable from https://pypi.org/project/pyobjc/.
The standard Python GUI toolkit is tkinter, based on the cross-platformTk toolkit (https://www.tcl.tk). An Aqua-native version of Tk is bundled with OSX by Apple, and the latest version can be downloaded and installed fromhttps://www.activestate.com; it can also be built from source.
wxPython is another popular cross-platform GUI toolkit that runs natively onMac OS X. Packages and documentation are available from https://www.wxpython.org.
PyQt is another popular cross-platform GUI toolkit that runs natively on MacOS X. More information can be found athttps://riverbankcomputing.com/software/pyqt/intro.
4.5. Distributing Python Applications on the Mac¶
Numpy Download
The standard tool for deploying standalone Python applications on the Mac ispy2app. More information on installing and using py2app can be foundat http://undefined.org/python/#py2app.
4.6. Other Resources¶
The MacPython mailing list is an excellent support resource for Python users anddevelopers on the Mac:
Another useful resource is the MacPython wiki:
How To Numpy For Python 3.6 Mac Os
Nearly every scientist working in Python draws on the power of NumPy.
NumPy brings the computational power of languages like C and Fortran to Python, a language much easier to learn and use. With this power comes simplicity: a solution in NumPy is often clear and elegant.
Quantum Computing Statistical Computing Signal Processing Image Processing 3-D Visualization Symbolic Computing Astronomy Processes Cognitive Psychology QuTiP Pandas SciPy Scikit-image Mayavi SymPy AstroPy PsychoPy PyQuil statsmodels PyWavelets OpenCV Napari SunPy Qiskit Seaborn SpacePy Bioinformatics Bayesian Inference Mathematical Analysis Simulation Modeling Multi-variate Analysis Geographic Processing Interactive Computing BioPython PyStan SciPy PyDSTool PyChem Shapely Jupyter Scikit-Bio PyMC3 SymPy GeoPandas IPython PyEnsembl cvxpy Folium Binder FEniCS NumPy's API is the starting point when libraries are written to exploit innovative hardware, create specialized array types, or add capabilities beyond what NumPy provides.
Array Library Capabilities & Application areas Dask Distributed arrays and advanced parallelism for analytics, enabling performance at scale. CuPy NumPy-compatible array library for GPU-accelerated computing with Python. JAX Composable transformations of NumPy programs: differentiate, vectorize, just-in-time compilation to GPU/TPU. Xarray Labeled, indexed multi-dimensional arrays for advanced analytics and visualization Sparse NumPy-compatible sparse array library that integrates with Dask and SciPy's sparse linear algebra. PyTorch Deep learning framework that accelerates the path from research prototyping to production deployment. TensorFlow An end-to-end platform for machine learning to easily build and deploy ML powered applications. MXNet Deep learning framework suited for flexible research prototyping and production. Arrow A cross-language development platform for columnar in-memory data and analytics. xtensor Multi-dimensional arrays with broadcasting and lazy computing for numerical analysis. XND Develop libraries for array computing, recreating NumPy's foundational concepts. uarray Python backend system that decouples API from implementation; unumpy provides a NumPy API. TensorLy Tensor learning, algebra and backends to seamlessly use NumPy, MXNet, PyTorch, TensorFlow or CuPy. NumPy lies at the core of a rich ecosystem of data science libraries. A typical exploratory data science workflow might look like:
- Extract, Transform, Load: Pandas, Intake, PyJanitor
- Exploratory analysis: Jupyter, Seaborn, Matplotlib, Altair
- Model and evaluate: scikit-learn, statsmodels, PyMC3, spaCy
- Report in a dashboard: Dash, Panel, Voila
For high data volumes, Dask and Ray are designed to scale. Stable deployments rely on data versioning (DVC), experiment tracking (MLFlow), and workflow automation (Airflow and Prefect).
NumPy forms the basis of powerful machine learning libraries like scikit-learn and SciPy. As machine learning grows, so does the list of libraries built on NumPy. TensorFlow’s deep learning capabilities have broad applications — among them speech and image recognition, text-based applications, time-series analysis, and video detection. PyTorch, another deep learning library, is popular among researchers in computer vision and natural language processing. MXNet is another AI package, providing blueprints and templates for deep learning.
Statistical techniques called ensemble methods such as binning, bagging, stacking, and boosting are among the ML algorithms implemented by tools such as XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost — one of the fastest inference engines. Yellowbrick and Eli5 offer machine learning visualizations.
NumPy is an essential component in the burgeoning Python visualization landscape, which includes Matplotlib, Seaborn, Plotly, Altair, Bokeh, Holoviz, Vispy, and Napari, to name a few.
NumPy's accelerated processing of large arrays allows researchers to visualize datasets far larger than native Python could handle.